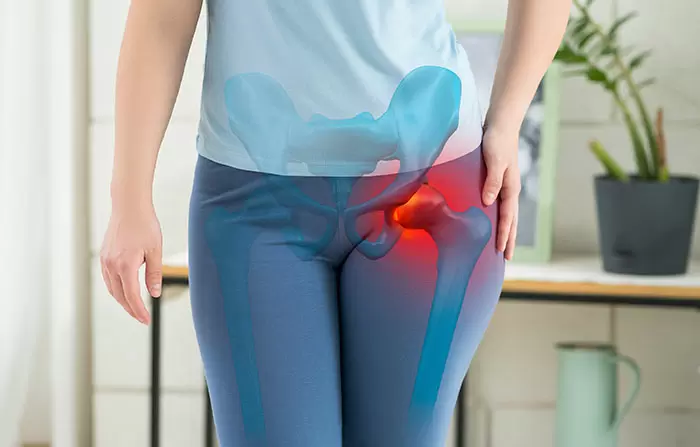
Undergoing a revision hip replacement surgery is a significant decision that can greatly improve your quality of life. This procedure is typically necessary when a previously implanted hip joint begins to wear out or fails to function properly, leading to pain and mobility issues. Understanding the key considerations before opting for this surgery is crucial for making informed decisions and achieving successful outcomes.
Understanding Revision Hip Replacement Surgery
Revision hip replacement surgery is a procedure performed to replace a worn-out or failed hip implant. This becomes necessary when the original implant no longer functions correctly, often due to wear and tear over time or complications such as implant loosening or infection. Unlike the initial hip replacement, which is intended to last for decades, revision surgery aims to restore the hip’s function and alleviate pain.
Eligibility and Pre-Surgery Assessment
Before undergoing revision hip replacement, it’s essential to determine whether you are a suitable candidate. Orthopedic surgeons typically assess eligibility based on factors such as the extent of hip damage, overall health, and medical history. This assessment often includes imaging tests (such as X-rays or MRI scans) to evaluate the condition of the hip joint and surrounding bone structure. Consulting with an orthopedic specialist is crucial to discuss individual circumstances and determine the best course of action.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, revision hip replacement carries certain risks and potential complications. These may include infection, blood clots, nerve damage, and issues related to anesthesia. Compared to initial hip replacement surgery, revision procedures can be more complex due to factors like bone loss or scar tissue from previous surgeries. Understanding these risks and discussing them with your healthcare team can help mitigate potential complications and prepare you for the recovery process.
Surgical Procedure Overview
The revision hip replacement surgery involves several key steps:
- Implant Removal: The old or damaged hip implant is carefully removed.
- Bone Preparation: The surgeon prepares the bone surfaces to receive the new implant.
- Implant Placement: New components (such as a metal shell, plastic liner, and ceramic or metal ball) are securely placed to restore hip function.
- Closure: The incision is closed, and post-operative care begins.
Advancements in surgical techniques, including minimally invasive approaches, have improved outcomes and reduced recovery times for many patients.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from revision hip replacement surgery varies depending on individual health and the complexity of the procedure. Initially, patients may require a hospital stay to monitor recovery and manage pain. Physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises are crucial for restoring strength, flexibility, and mobility in the hip joint. It’s important to follow post-operative instructions provided by healthcare providers to optimize recovery and achieve the best possible outcome.
Lifestyle Adjustments and Long-Term Outlook
After revision hip replacement, certain lifestyle adjustments may be necessary to protect the new implant and maintain hip health. This may include avoiding high-impact activities, maintaining a healthy weight, and incorporating joint-friendly exercises into daily routines. While the goal of revision surgery is to improve hip function and alleviate pain, individual outcomes can vary. Long-term follow-up with orthopedic specialists helps monitor hip health and address any concerns that may arise over time.
Takeaway
Deciding to undergo revision hip replacement surgery requires careful consideration of the factors discussed above. By understanding the procedure, assessing eligibility, acknowledging potential risks, and planning for recovery and rehabilitation, patients can make informed decisions in collaboration with their healthcare providers. Consultation with an orthopedic specialist is essential for personalized advice and guidance tailored to individual circumstances.