Understanding Green Roof Systems
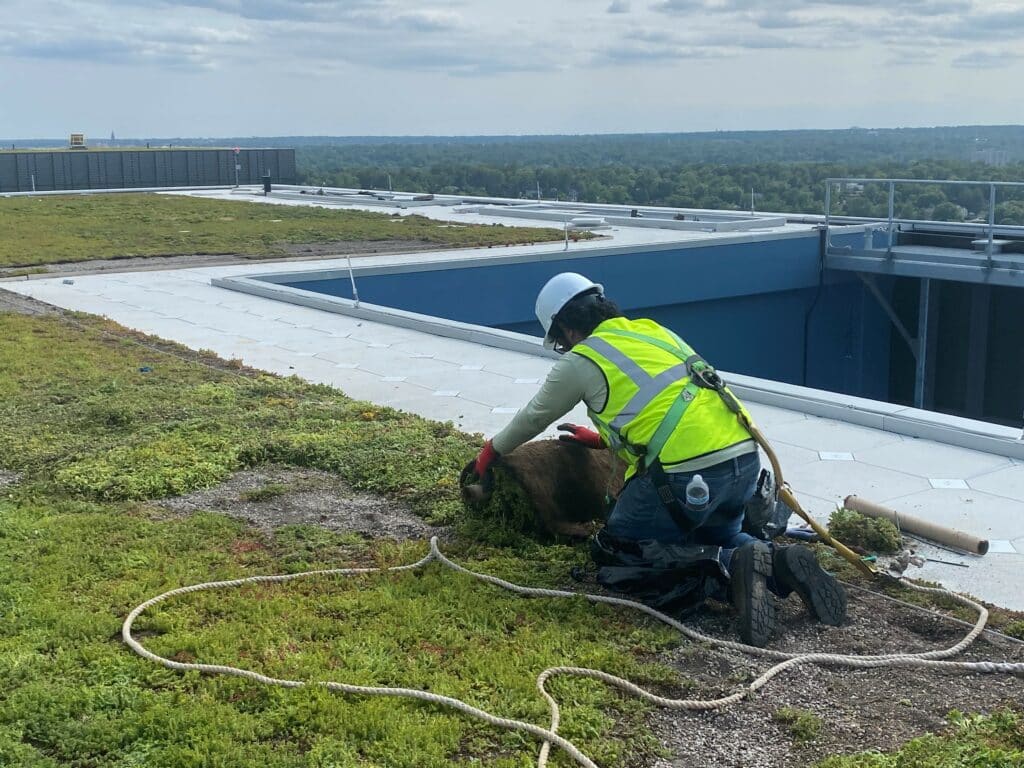
A green roof system is a roofing solution that incorporates living vegetation on top of a building. Unlike traditional roofs, which are typically made of asphalt, concrete, or metal, a green roof system provides multiple layers designed to support plant life, including a waterproof membrane, drainage layer, growing medium, and vegetation. These systems are generally categorized into three types: extensive, semi-intensive, and intensive. Extensive green roofs are lightweight and require minimal maintenance, often featuring low-growing plants such as sedums. Semi-intensive roofs strike a balance with slightly deeper soil and more diverse plantings. Intensive green roofs resemble rooftop gardens with shrubs, trees, and recreational spaces but require substantial structural support and regular care. Each type offers unique benefits depending on the building’s purpose, climate, and structural capacity. Green roof systems are not just aesthetic upgrades; they represent a strategic investment in sustainability, energy efficiency, and urban resilience.
Environmental Benefits of Green Roof Systems
One of the most notable benefits of a green roof system is its ability to reduce the urban heat island effect. By absorbing sunlight and providing a cooling layer, green roofs help lower surrounding temperatures and improve the comfort of urban spaces. These roofs also enhance air quality by capturing airborne pollutants and absorbing carbon dioxide, making cities healthier for residents. Stormwater management is another critical advantage, as the plants and growing medium absorb rainfall, reducing runoff and mitigating the risk of flooding. Green roofs also support urban biodiversity by creating habitats for birds, insects, and pollinators, which is especially valuable in heavily developed areas. Additionally, they help decrease noise pollution by providing a sound-absorbing layer on rooftops. By integrating green roof systems into urban design, communities can achieve a healthier, more sustainable environment while contributing to long-term ecological balance.
Economic and Energy Advantages
Green roof systems are not only environmentally friendly but also economically beneficial. They act as natural insulators, reducing the building’s heating and cooling costs by regulating indoor temperatures throughout the year. A properly installed green roof can extend the lifespan of roofing materials by protecting them from UV rays, extreme temperatures, and weather-related wear and tear. This leads to reduced repair and replacement costs over time. Buildings with green roofs often experience increased property value due to their sustainability features and aesthetic appeal. Some local governments and municipalities offer financial incentives, tax breaks, or rebates for buildings that implement green roofs, making them more affordable for property owners. The investment in a green roof system can also attract environmentally conscious tenants or buyers, enhancing the marketability of residential or commercial properties. The combined energy, maintenance, and environmental benefits make green roofs a practical long-term investment.
Installation Process of a Green Roof System
Installing a green roof system requires careful planning and evaluation. A structural assessment of the building is crucial to determine whether it can support the additional weight of soil, plants, and water. Once feasibility is confirmed, selecting the right type of green roof is the next step. The installation process begins with a waterproofing layer to prevent leaks, followed by a drainage layer that allows excess water to flow away efficiently. Next is the growing medium, designed to support healthy plant growth while being lightweight and nutrient-rich. Finally, vegetation is planted according to the chosen design, whether it involves simple ground cover plants or more complex combinations of shrubs and flowers. Common challenges include ensuring proper drainage, preventing root damage to the waterproof membrane, and maintaining plant health during the initial growth period. Working with experienced professionals ensures that the green roof system is installed correctly and delivers its full benefits for years to come.
Maintenance and Care
A green roof system requires regular maintenance to ensure its longevity and performance. Routine inspections help identify drainage problems, plant health issues, and any signs of structural stress. Watering is necessary, particularly during dry spells, to support plant growth and maintain soil moisture. Fertilization may be needed depending on the type of vegetation and local soil conditions. Weed control is important to prevent unwanted plants from overtaking the green roof system. Seasonal considerations, such as leaf removal in the fall and frost protection in the winter, also play a role in maintaining the system. Some plants may need replacement over time due to natural aging or extreme weather conditions. Proper maintenance ensures that the green roof continues to provide environmental, economic, and aesthetic benefits.
Innovative Uses of Green Roof Systems
Beyond environmental and economic advantages, green roof systems offer innovative opportunities for urban spaces. Rooftop gardens can create recreational areas for building occupants, offering a serene escape in busy urban settings. Urban agriculture is becoming increasingly popular, with green roofs being used to grow vegetables, herbs, and edible plants. These gardens promote local food production and reduce the carbon footprint associated with transporting produce. Green roofs can also integrate with solar panels, combining renewable energy generation with natural insulation. Some buildings incorporate green roofs as part of wellness initiatives, providing calming green spaces that improve mental health. By thinking creatively, property owners can transform rooftops into multifunctional spaces that deliver environmental, social, and economic value.
Costs and Investment Considerations
The cost of installing a green roof system varies depending on the type, scale, and complexity of the project. Extensive roofs are generally more affordable, while intensive roofs with diverse plantings and structural reinforcements are more expensive. Long-term maintenance costs should also be considered, including irrigation, fertilization, and occasional plant replacement. Despite the higher initial investment, green roofs offer a strong return through energy savings, reduced maintenance of conventional roofing materials, and potential financial incentives. They can also enhance property marketability and attract environmentally conscious tenants or buyers. Compared to traditional roofs, the lifetime value of a green roof system often outweighs the upfront costs. Property owners should evaluate both immediate and long-term benefits when considering this investment.
Regulatory and Building Code Considerations
Local regulations and building codes can influence the design and installation of a green roof system. Some municipalities require permits for rooftop modifications or impose specific structural and safety standards. Compliance with these regulations ensures that the green roof is both safe and sustainable. Additionally, environmental certifications such as LEED or recognition from green building councils can provide credibility and potential financial incentives. It is important to work with professionals who understand local codes and can navigate permitting requirements effectively. Adhering to regulations also ensures the roof’s longevity and reduces liability concerns. Building owners should research local policies before committing to a green roof project. With proper planning, a green roof system can meet all legal requirements while maximizing environmental and economic benefits.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How long does a green roof system last? A well-maintained green roof can last 30 to 50 years, significantly longer than traditional roofing materials.
Can any building support a green roof? Structural evaluation is essential. Not all buildings can support the additional weight of soil, plants, and water, especially intensive green roofs.
What plants are best for green roofs? Low-maintenance, drought-resistant plants like sedums, grasses, and small shrubs are commonly used. Intensive roofs allow for a wider variety of plants.
How does a green roof handle heavy rainfall or snow? Proper drainage layers and slope design ensure that excess water and snowmelt are managed efficiently, preventing damage.
Is a green roof system suitable for residential homes? Yes, extensive and semi-intensive green roofs can be installed on residential homes if the structure is suitable, providing both environmental and aesthetic benefits.
Takeaway
Green roof systems offer a compelling combination of environmental, economic, and aesthetic advantages. They improve urban air quality, reduce energy consumption, manage stormwater, and enhance property value while creating versatile green spaces. By carefully considering installation, maintenance, and regulatory requirements, property owners can enjoy long-lasting benefits. Whether for commercial buildings, residential homes, or urban agriculture projects, investing in a green roof system contributes to sustainability, resilience, and a healthier living environment.