Understanding Non-Healing Wounds
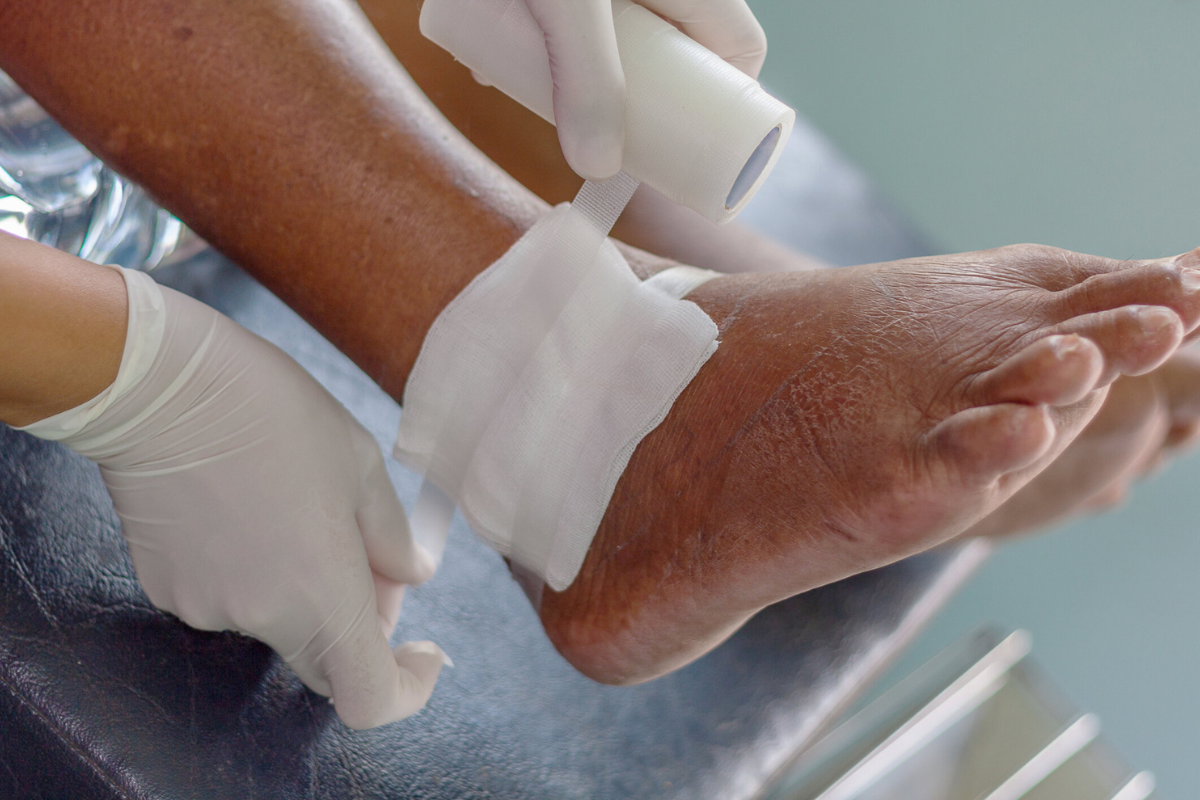
Non-healing wounds can be frustrating and debilitating, especially when they interfere with daily activities and overall mobility. These wounds, often referred to as chronic wounds, are injuries that fail to progress through the normal stages of healing within an expected timeframe, usually around 4 to 6 weeks. Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds focuses on addressing underlying factors that prevent healing, such as poor blood circulation, infections, diabetes, or tissue damage. The prolonged presence of a chronic wound can increase the risk of complications like deep tissue infections, sepsis, or even amputation if not managed appropriately. Identifying the root cause of the wound is critical for developing a targeted treatment plan. Chronic wounds often develop in areas that bear weight or experience repeated trauma, such as the feet, legs, or joints. Understanding the nature of these wounds is the first step in restoring function and promoting full recovery.
Signs That Indicate the Need for Orthopedic Intervention
Persistent pain, swelling, redness, or discharge around a wound often signals the need for professional orthopedic intervention. In some cases, patients may notice that a wound fails to close despite regular care and dressing changes. The presence of odor, tissue discoloration, or necrotic tissue is also a red flag that specialized treatment is required. Difficulty in walking or bearing weight can further indicate that the wound is affecting joint function or bone integrity. Orthopedic specialists are trained to evaluate not just the surface wound, but also underlying musculoskeletal structures to ensure comprehensive care. Early identification of warning signs can significantly improve the chances of successful healing and prevent more severe complications. Patients are encouraged to seek expert care as soon as a wound shows signs of delayed healing to maximize recovery outcomes.
Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Wound Management
Orthopedic specialists play a central role in managing non-healing wounds, often working in coordination with other healthcare professionals. A multidisciplinary approach may involve vascular surgeons, podiatrists, infectious disease experts, and physical therapists to address the complex factors contributing to chronic wounds. Accurate diagnosis typically involves imaging studies, blood tests, and detailed wound assessments to determine the extent of tissue damage. Once the root causes are identified, specialists create personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient’s needs. The goal is to restore tissue integrity, prevent infection, and support overall musculoskeletal health. Regular follow-ups and adjustments to the treatment plan ensure that progress is closely monitored. Orthopedic intervention is most effective when paired with patient education and lifestyle modifications that support wound healing.
Advanced Orthopedic Treatment Options
Several advanced treatment options are available for managing non-healing wounds through orthopedic care. Surgical interventions such as debridement remove dead or infected tissue, promoting the growth of healthy tissue. Skin grafts and flap surgeries may be necessary when extensive tissue loss is present, especially over joints or weight-bearing areas. Non-surgical treatments also play a vital role, including negative pressure wound therapy, which helps draw out fluids, reduce swelling, and accelerate tissue regeneration. Specialized dressings containing growth factors or antimicrobial agents can protect the wound and enhance healing. Emerging therapies, such as stem cell treatments and bioengineered skin substitutes, are showing promising results in chronic wound management. Combining these approaches allows orthopedic specialists to tailor treatments to the wound’s severity and the patient’s overall health status.
Post-Treatment Care and Rehabilitation
Post-treatment care is critical to ensure that the wound heals completely and complications are minimized. Monitoring the wound regularly for signs of infection, changes in color, or delayed healing is essential. Patients are often instructed on proper dressing techniques, hygiene practices, and when to seek medical attention for complications. Physical therapy may be recommended to restore mobility, strength, and joint function, especially if the wound has affected weight-bearing areas. Maintaining optimal nutrition, controlling blood sugar levels, and avoiding smoking can significantly improve healing outcomes. Patients may also need guidance on modifying activities to prevent repeated trauma to the affected area. Ongoing support and education empower patients to take an active role in their recovery, enhancing both short-term and long-term results.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Recurrence
Preventing recurrence of non-healing wounds is an important aspect of orthopedic care. Routine medical check-ups allow early identification of conditions that may delay healing, such as poor circulation or uncontrolled diabetes. Patients are encouraged to follow daily skin and foot care routines, including moisturizing, inspecting for early signs of injury, and wearing protective footwear. Managing underlying conditions is crucial, as untreated diabetes or vascular disorders can contribute to chronic wounds. Orthopedic specialists often provide guidance on safe physical activities to maintain mobility without stressing vulnerable areas. Educating patients on warning signs and preventive strategies reduces the likelihood of wound recurrence. A proactive approach combining regular monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, and adherence to medical advice is essential for long-term success.
Patient Education and Support
Patient education and support are integral to the effectiveness of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Teaching patients how to care for their wounds at home, including proper dressing techniques and hygiene practices, reduces the risk of infection and promotes healing. Explaining the importance of following the prescribed treatment plan ensures that patients remain engaged and compliant. Emotional and psychological support is equally important, as living with a chronic wound can lead to anxiety, frustration, or depression. Orthopedic specialists often work with patients to set realistic healing goals and provide encouragement throughout the recovery process. Empowering patients with knowledge and tools helps them make informed decisions and take an active role in their care. Long-term support fosters independence while maximizing the effectiveness of medical interventions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What makes a wound “non-healing”?
A non-healing wound is one that fails to progress through the typical stages of healing within an expected timeframe, often due to underlying medical conditions, infection, poor circulation, or repeated trauma.
How long does orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds typically take?
The duration varies depending on the wound’s severity, underlying causes, and chosen treatment. Some wounds may heal within weeks, while others require months of ongoing care and monitoring.
Are there non-surgical alternatives for chronic wounds?
Yes, non-surgical options include negative pressure wound therapy, specialized dressings, growth factor treatments, and emerging therapies like stem cells and bioengineered skin substitutes.
Can lifestyle changes speed up the healing process?
Absolutely. Proper nutrition, controlling blood sugar, quitting smoking, managing weight, and avoiding repeated trauma can all support faster wound healing and reduce complications.
When should a patient seek specialized orthopedic care?
Patients should consult an orthopedic specialist if a wound fails to show improvement after a few weeks, exhibits infection signs, causes mobility issues, or if there is a history of chronic illness affecting healing.