Understanding Non-Healing Wounds and Their Challenges
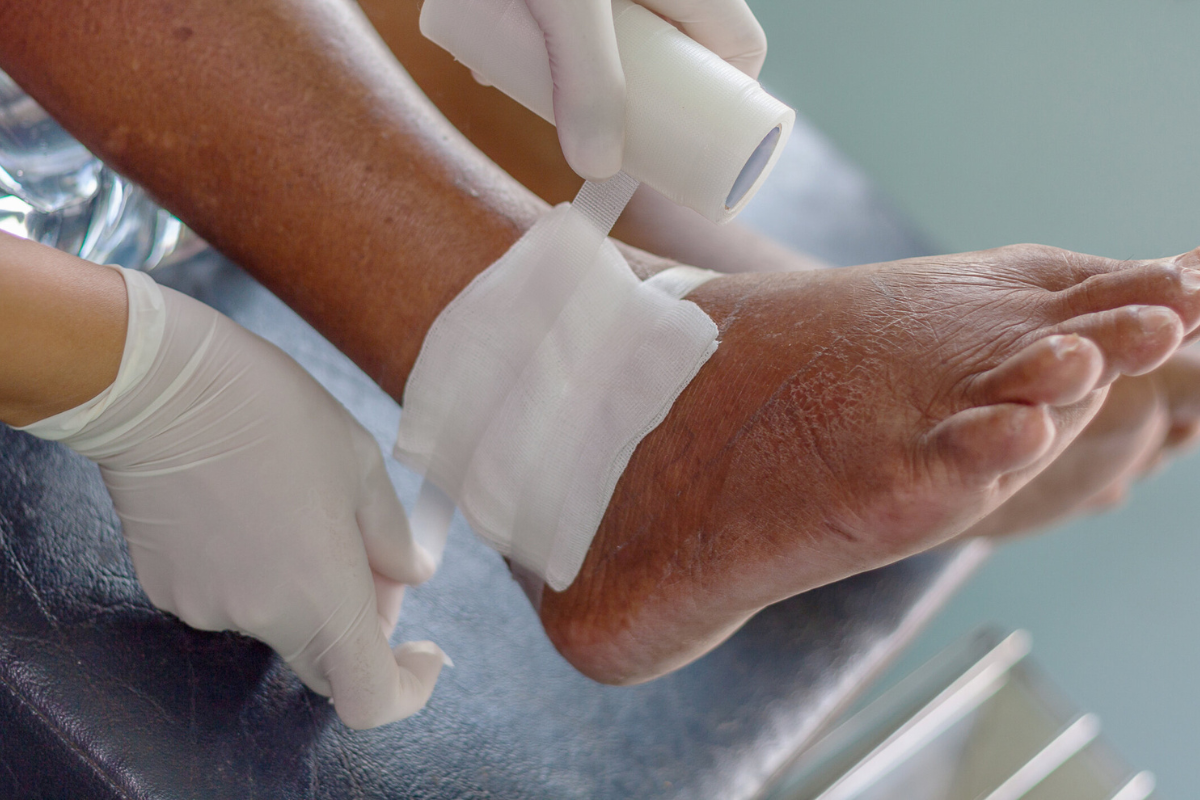
Non-healing wounds, also called chronic wounds, are injuries that fail to show measurable progress toward healing within weeks or even months. Unlike minor cuts and scrapes that close quickly, these wounds linger due to underlying medical complications. Diabetes, vascular disease, immune system disorders, and repeated trauma are among the most common reasons wounds do not heal properly. Without appropriate medical attention, such wounds may worsen, leading to infections that can spread into deeper tissues and even the bone. The consequences extend beyond physical discomfort, as patients may face limited mobility, reduced independence, and psychological distress. Left unchecked, some non-healing wounds can even result in severe disability or amputation. This is why understanding the underlying cause and seeking timely specialized care is essential for recovery and improved quality of life.
The Role of Orthopedic Specialists in Wound Management
Orthopedic doctors are uniquely positioned to manage non-healing wounds because of their expertise in the musculoskeletal system. Unlike general wound care practitioners, they evaluate not only the wound itself but also how bones, joints, and connective tissues may be contributing to slow healing. For example, diabetic foot ulcers often involve complications with bone alignment, nerve damage, and pressure points that require orthopedic solutions. Similarly, post-surgical wounds following joint replacements or fractures can benefit from targeted orthopedic care. Orthopedic specialists can provide a holistic approach that addresses both the visible wound and the hidden structural issues causing it. Their role often involves collaborating with vascular surgeons, endocrinologists, and physical therapists to create a comprehensive treatment plan. By focusing on stability, alignment, and circulation, orthopedic doctors enhance the body’s natural ability to heal. This level of specialized attention can mean the difference between ongoing pain and a return to mobility.
Advanced Diagnostic Approaches in Orthopedic Care
When a patient presents with a non-healing wound, orthopedic doctors start with thorough diagnostic evaluations to identify all contributing factors. Imaging tools such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans help determine whether underlying bone or joint problems are preventing healing. Blood flow assessments, including Doppler studies, are often used to measure circulation, since poor oxygen supply significantly hinders wound closure. Orthopedic specialists may also order nerve function tests to assess whether conditions like neuropathy are worsening the wound. Infection is another critical concern, and bone scans or biopsies may be required to detect osteomyelitis, an infection of the bone that complicates healing. These diagnostic steps allow doctors to tailor treatment plans to each patient’s unique situation rather than applying a one-size-fits-all solution. Early and accurate diagnosis plays a major role in preventing further complications. With advanced imaging and testing, orthopedic specialists ensure no underlying problem goes unaddressed.
Orthopedic Treatment Options for Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds typically involves a combination of surgical and non-surgical interventions. Surgical debridement, the removal of dead or infected tissue, is often the first step to promote healthy tissue growth. In more severe cases, skin grafts or reconstructive procedures may be recommended to restore damaged areas. Orthopedic hardware such as external fixators or braces may be used to stabilize fractures or relieve pressure from wounds in high-stress areas like the feet. Beyond surgery, advanced wound dressings with antimicrobial properties and negative pressure wound therapy help accelerate healing. These techniques not only protect the wound but also encourage blood flow and tissue regeneration. Antibiotics are frequently prescribed for infections, with careful monitoring to ensure they target the correct bacteria. Each treatment method is chosen based on the wound’s severity, location, and the patient’s overall health. This personalized approach makes orthopedic care highly effective for stubborn wounds that resist traditional treatment.
Rehabilitation and Supportive Care in Orthopedic Wound Healing
Successful healing involves more than closing the wound; it requires rehabilitation and supportive care to restore function and prevent recurrence. Physical therapy is often prescribed to improve circulation, strengthen surrounding muscles, and encourage mobility without putting excessive pressure on the wound. Patients may also receive guidance on nutrition, as proper protein, vitamin, and mineral intake is crucial for tissue repair. Pain management is another priority, with orthopedic doctors using both medications and non-pharmacological methods to keep patients comfortable during recovery. Assistive devices such as custom orthotics, walkers, or braces may be recommended to reduce stress on vulnerable areas and give wounds the best chance to heal. Lifestyle adjustments, including smoking cessation and blood sugar control for diabetic patients, are strongly encouraged as part of a long-term care plan. Supportive care ensures that patients not only recover from their current wound but also avoid future complications. By combining medical treatment with holistic strategies, orthopedic specialists help patients achieve sustainable healing.
Innovations in Orthopedic Wound Treatment
Medical advancements continue to transform orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, offering patients new hope for recovery. Bioengineered skin substitutes made from living cells can be applied to stubborn wounds, stimulating growth and providing coverage. Growth factors and protein-based therapies are being used to enhance the body’s natural healing mechanisms. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy, where patients breathe pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, has shown promising results in increasing tissue oxygenation and speeding recovery. Stem cell therapy is another area of innovation, with studies exploring its ability to regenerate damaged tissue and promote long-term healing. Some orthopedic centers are even using 3D-printed grafts to repair complex wounds and reconstruct damaged bone and soft tissue. These breakthroughs represent a significant step forward in wound management, giving patients access to treatments that were once unavailable. Innovations continue to expand options for those who previously faced limited outcomes.
Preventive Orthopedic Strategies to Avoid Non-Healing Wounds
Prevention is an important part of orthopedic wound management, as stopping wounds from becoming chronic is always preferable to treatment. Early intervention after injuries such as fractures or sprains can reduce the likelihood of long-term complications. For diabetic patients, routine foot care and regular orthopedic evaluations are strongly recommended to avoid ulcers and pressure wounds. After orthopedic surgeries, proper wound care practices such as keeping incisions clean and protected are essential to avoid infections. Patients are often advised to monitor for swelling, redness, or unusual pain, which may signal delayed healing. Maintaining bone and joint health through exercise, weight management, and proper footwear can also lower the risk of wound development. Orthopedic specialists emphasize patient education, teaching individuals how to care for their musculoskeletal system to support long-term wellness. Preventive strategies empower patients to play an active role in protecting themselves against chronic wounds.
When to Seek an Orthopedic Doctor for Non-Healing Wounds
Recognizing when to seek specialized care can make a major difference in outcomes. If a wound shows no signs of healing after two to four weeks of proper care, an orthopedic consultation may be necessary. Additional warning signs include increasing pain, foul odor, drainage, swelling, or visible exposure of bone or tendon. Patients with diabetes, vascular disease, or a history of orthopedic surgery should be especially vigilant. Delayed treatment can lead to worsening infections, deeper tissue involvement, and permanent loss of function. During an orthopedic appointment, patients can expect a detailed examination, advanced diagnostic testing, and a tailored treatment plan. Seeking timely orthopedic care not only helps heal current wounds but also prevents them from becoming lifelong complications. By understanding when to escalate care, patients can take proactive steps toward recovery and mobility.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What types of wounds require orthopedic treatment?
Non-healing wounds associated with bone, joint, or musculoskeletal complications—such as diabetic foot ulcers, post-surgical wounds, pressure sores, and fractures with delayed healing—often require orthopedic expertise.
How long does orthopedic wound healing usually take?
The timeline varies depending on the wound’s severity, location, and underlying health conditions. While some wounds improve in weeks with proper care, others may take several months to fully recover.
Can non-healing wounds always be treated without surgery?
Not all cases require surgery, but some wounds benefit from surgical interventions like debridement, grafting, or reconstruction. The decision depends on the wound’s depth, infection status, and overall patient health.
What’s the difference between a wound care clinic and orthopedic wound treatment?
General wound care clinics treat a wide variety of skin injuries, while orthopedic wound treatment focuses on cases involving bones, joints, and musculoskeletal complications that need specialized expertise.
Does insurance typically cover orthopedic wound procedures?
Most insurance plans cover medically necessary orthopedic treatments for non-healing wounds, but coverage may vary depending on the procedure, provider, and insurance policy. Patients are advised to confirm benefits with their provider.