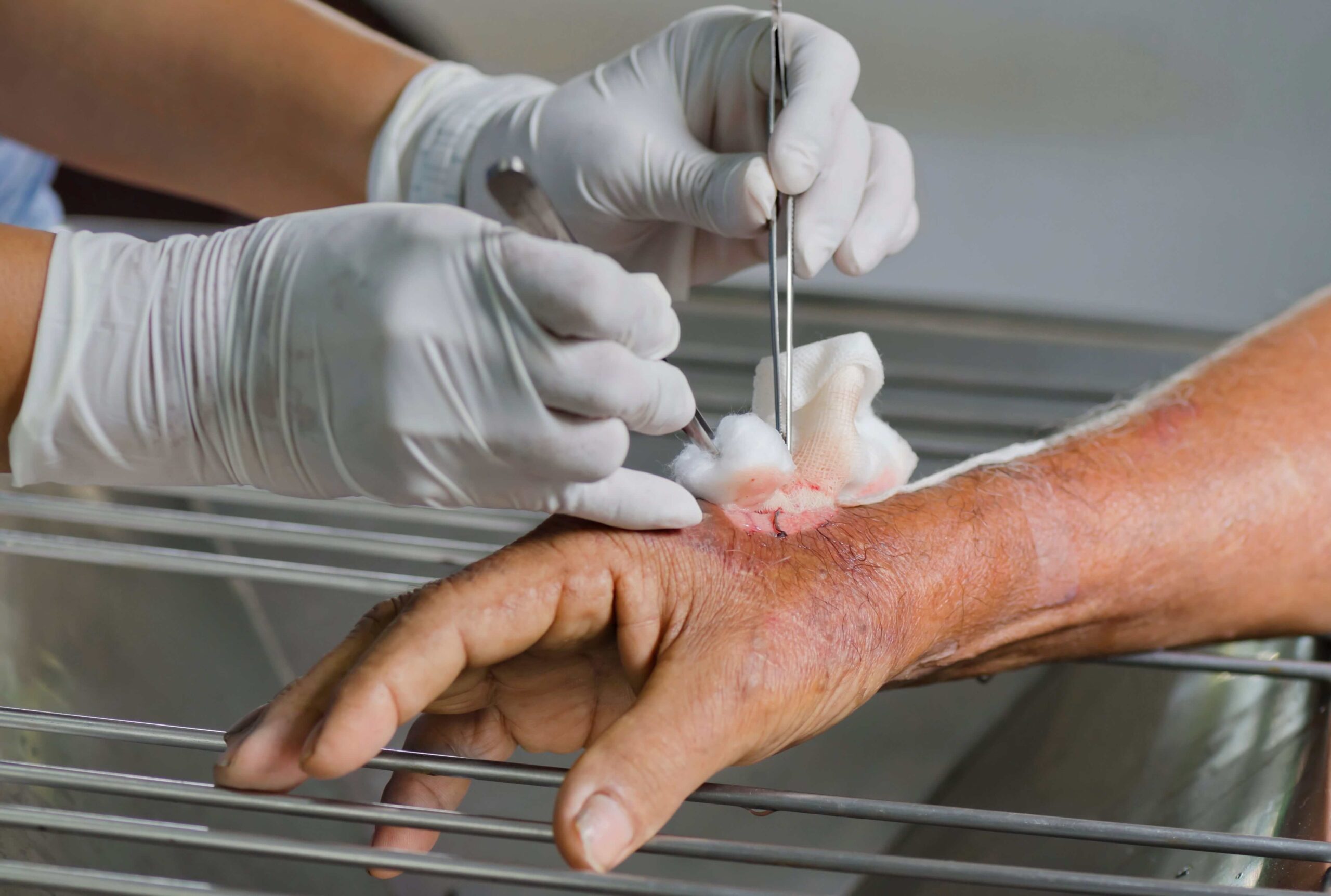
Wound debridement services play a crucial role in managing wounds that fail to heal properly or show signs of infection. This process involves the removal of dead, damaged, or infected tissue to encourage healthy tissue growth and improve the body’s ability to heal. Without proper debridement, wounds can worsen, leading to complications such as infection, prolonged pain, or even systemic illness. Understanding what wound debridement involves helps patients and caregivers make informed decisions about treatment options. Many types of wounds, including diabetic ulcers, pressure sores, and traumatic injuries, benefit significantly from these services. Wound care treatment using debridement is often part of a broader management plan aimed at restoring skin integrity and preventing further complications. Knowing the basics of wound debridement can reduce anxiety and improve cooperation during treatment.
Types of Wound Debridement Services
Wound debridement services include several methods, each suited to different wound types and patient needs. Surgical debridement is often used for deep or severe wounds and involves the precise removal of unhealthy tissue by a healthcare professional. Mechanical debridement uses physical force, such as wet-to-dry dressings or irrigation, to clean the wound. Enzymatic debridement employs topical agents that break down necrotic tissue chemically and is often a gentler option for patients with sensitive wounds. Autolytic debridement takes advantage of the body’s natural enzymes and moisture to dissolve dead tissue, typically through specialized dressings that maintain a moist environment. Biological debridement, though less common, uses medical-grade maggots that selectively consume necrotic tissue, promoting healing without damaging healthy tissue. Each technique has specific advantages and is chosen based on wound characteristics, patient health status, and healing goals. Healthcare professionals will evaluate these factors to recommend the most effective debridement approach.
Indications for Wound Debridement
Knowing when wound debridement services are necessary can prevent complications and speed up recovery. Typically, wounds that do not heal after a few weeks, contain dead tissue, or show signs of infection require debridement. Chronic wounds, such as diabetic foot ulcers and pressure sores, are especially prone to developing necrotic tissue that delays healing. Symptoms signaling the need for debridement include foul odor, increased pain, swelling, redness around the wound, and the presence of thick, discolored tissue. Healthcare providers assess these symptoms alongside the patient’s overall health, including circulation and immune function, to determine if debridement is appropriate. Early intervention often prevents more invasive treatments later on and reduces the risk of severe infection or amputation in extreme cases. Patients with compromised immune systems or diabetes should be particularly vigilant about wound care and seek professional advice promptly.
What to Expect During Wound Debridement Services
Wound debridement procedures vary depending on the method used, but patients can expect a thorough, focused approach to removing unhealthy tissue while preserving healthy skin. Surgical debridement usually takes place in a clinical setting under local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. The provider will carefully excise or cut away dead tissue using sterile instruments. Mechanical methods might involve cleansing the wound with saline or applying dressings that dry and remove debris when changed. Enzymatic and autolytic options are less invasive, involving the application of topical agents or moisture-retentive dressings and may require multiple sessions over days or weeks. Biological debridement is performed under strict medical supervision, with maggots applied in a controlled manner and removed once the necrotic tissue is cleared. Throughout any debridement session, pain management is prioritized to keep patients comfortable. After treatment, wound monitoring and proper dressing changes are essential to support the healing process and detect any complications early.
Benefits and Risks of Wound Debridement
Receiving wound debridement services offers several important benefits that contribute to better overall outcomes. Removing dead tissue reduces bacterial buildup, lowering the risk of infection and sepsis. It also stimulates the formation of new, healthy tissue and improves blood circulation within the wound area, speeding up recovery. Debridement can relieve pain caused by pressure on damaged tissue and reduce unpleasant odors associated with necrotic wounds. However, like any medical procedure, there are potential risks. Some patients might experience bleeding, increased pain, or damage to surrounding healthy tissue if the procedure is not done carefully. Infection can occur if sterile techniques are not maintained. Choosing a skilled and experienced healthcare provider greatly minimizes these risks. Patients should communicate openly about any discomfort or concerns during the process to ensure appropriate care adjustments.
Advances in Wound Debridement Technology
Technology continues to improve the effectiveness and comfort of wound debridement services. Newer tools such as ultrasonic debridement devices use sound waves to selectively remove dead tissue while sparing healthy skin. Laser-assisted treatments are also emerging, offering precision and reducing recovery time. Telemedicine has expanded access to wound care specialists, allowing for remote monitoring and timely adjustments to treatment plans. Moisture-retentive dressings and advanced topical agents now support autolytic and enzymatic debridement methods with enhanced safety and effectiveness. Research into bioengineered tissues and regenerative medicine offers promising potential for future wound healing therapies. These innovations are helping healthcare providers offer tailored, patient-centered care that improves outcomes and patient satisfaction. Staying informed about technological advances can help patients and caregivers feel more confident in their treatment options.
How to Choose the Right Wound Debridement Service Provider
Selecting a qualified wound debridement service provider is essential for successful healing and minimizing risks. Look for healthcare professionals with specialized training and certifications in wound care and debridement techniques. Facilities should follow strict infection control protocols and offer a range of treatment options tailored to individual patient needs. During consultation, ask about the provider’s experience with wounds similar to yours and inquire how they manage pain and prevent complications. Personalized treatment plans that consider underlying health conditions, lifestyle, and healing goals lead to the best results. Access to ongoing support, including follow-up visits and patient education, is also important. Trust and open communication with your care team enhance cooperation and improve healing experiences. Making an informed choice helps ensure that wound debridement services provide the safest and most effective care possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Wound Debridement Services
Is wound debridement painful?
Pain levels vary depending on the type of debridement and individual pain tolerance. Surgical and mechanical debridement may cause discomfort, but providers use local anesthesia and pain relief strategies to minimize it. Enzymatic and autolytic methods are generally less painful.
How often does wound debridement need to be done?
The frequency depends on wound size, type, and healing progress. Some wounds require debridement only once, while others may need regular sessions over weeks or months.
Can wound debridement be done at home?
Certain types like autolytic debridement can be managed at home under professional guidance. Surgical and mechanical debridement typically require clinical settings to ensure safety.
What are the signs of infection after debridement?
Watch for increased redness, swelling, warmth, pain, pus, or a foul odor. Fever or chills may indicate a more serious infection requiring prompt medical attention.
How long does it take for wounds to heal after debridement?
Healing time varies widely based on wound size, patient health, and treatment quality. With proper care, many wounds begin to improve within days to weeks.