Understanding Forefoot Ulcers and Why They Develop
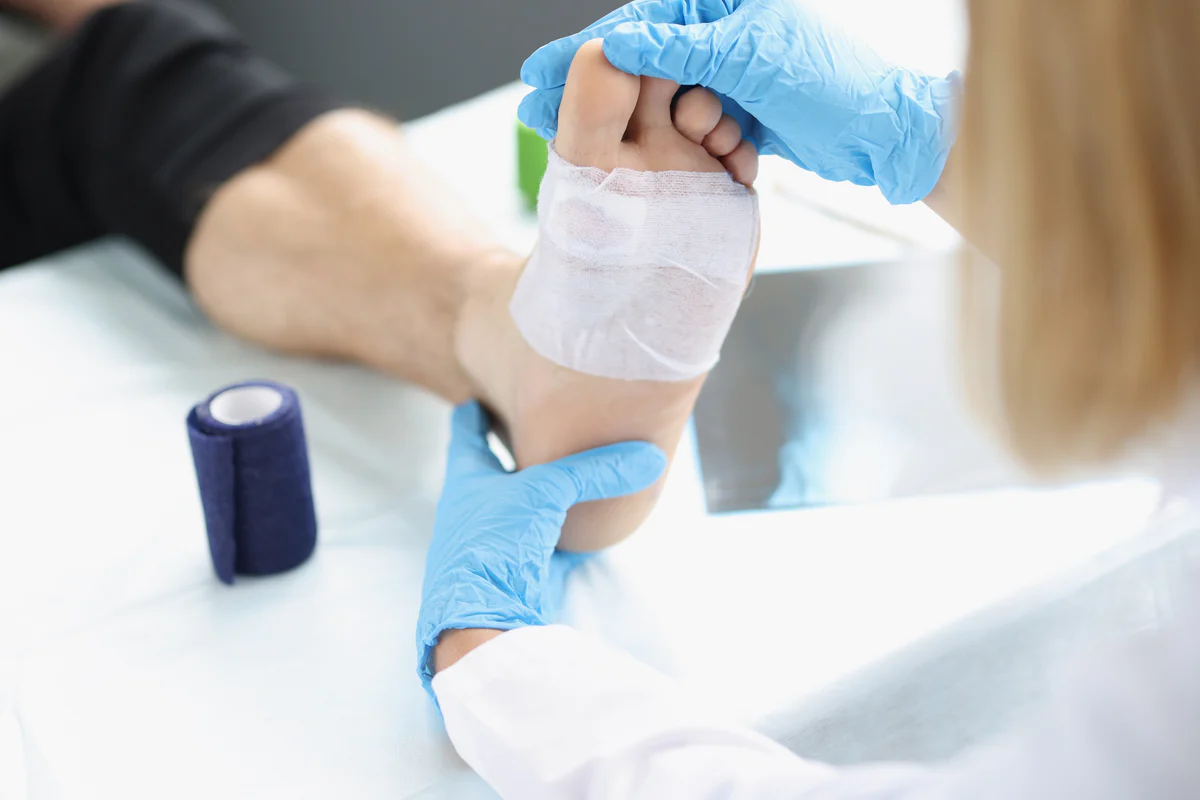
Forefoot ulcers are open sores or lesions that appear on the ball of the foot, toes, or metatarsal area. They differ from other foot wounds because they often develop in areas under continuous pressure or friction, making them harder to heal. These ulcers are commonly seen in people with diabetes, peripheral neuropathy, poor circulation, or structural foot deformities. Neuropathy can reduce the ability to feel pain or pressure, allowing ulcers to form without notice. Poor circulation slows healing and increases the risk of infection. Biomechanical abnormalities, such as bunions, hammertoes, or uneven weight distribution, contribute to localized stress on the forefoot. Early signs of forefoot ulcers include redness, swelling, persistent pain, and small blisters that may progress to deeper sores if left untreated.
How Orthopedic Medicine Addresses Forefoot Ulcers
Orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers focuses on addressing both the wound and the underlying structural issues that cause it. Foot and ankle specialists work to redistribute pressure across the foot to prevent further tissue damage. Orthopedic interventions aim to correct biomechanical imbalances that exacerbate ulcer formation. The role of orthopedics is not limited to treating the ulcer itself but also ensuring long-term foot health and mobility. Specialists often collaborate with podiatrists, vascular surgeons, and wound care teams for comprehensive care. Proper evaluation allows orthopedists to design personalized treatment plans that combine offloading, wound management, and corrective procedures. Orthopedic treatment also focuses on preventing recurrence and maintaining functional mobility.
Diagnostic Steps Before Orthopedic Treatment Begins
Before starting treatment, orthopedic specialists conduct a thorough assessment to determine the severity of the ulcer. This begins with a detailed physical examination to classify the wound and assess tissue health. Vascular evaluation is critical to determine blood flow and identify any circulation problems that could hinder healing. Imaging techniques, including X-rays, MRI, or ultrasound, may be used to detect underlying bone involvement, infections, or foot deformities. Identifying structural abnormalities helps orthopedists create effective treatment plans. In many cases, a multidisciplinary approach is recommended to manage complex ulcers involving neuropathy, vascular issues, or infection. Early and accurate diagnosis increases the chances of successful healing and reduces the risk of complications.
Conservative Orthopedic Treatment Options for Forefoot Ulcers
Conservative orthopedic treatments aim to relieve pressure on the ulcer and promote natural healing. One of the most common methods is offloading, which redistributes weight away from the affected area. Offloading techniques include:
- Custom orthotics designed to support the arch and cushion pressure points
- Total contact casting to immobilize and protect the foot
- Specialized therapeutic shoes that reduce friction and stress
Debridement, the process of removing dead tissue, is often performed to accelerate healing. Orthopedic padding, gel inserts, and pressure-relief devices provide additional protection. Wound dressings and infection control measures are integrated into the orthopedic care plan. Patients are advised to limit weight-bearing activities and follow mobility guidelines set by their orthopedic specialist. Conservative management can be highly effective, particularly when combined with lifestyle changes and diligent foot care.
Surgical Orthopedic Interventions for Complex or Non-Healing Forefoot Ulcers
When conservative treatments fail, surgical intervention may become necessary. Surgery focuses on correcting structural problems that contribute to ulcer formation and persistent pressure. Common procedures include:
- Osteotomies to realign bones and improve foot structure
- Tendon lengthening to balance tension and reduce pressure
- Joint resection or reconstruction for severe deformities
Surgical approaches also aim to offload the affected area permanently, reducing the likelihood of recurrence. Infection management is critical during surgery, especially in diabetic patients or those with compromised circulation. Postoperative care includes protective footwear, orthotics, and physical therapy to restore mobility. Orthopedic surgery is carefully tailored to the patient’s overall health, foot anatomy, and risk factors to maximize healing outcomes.
Preventing Recurrence Through Orthopedic Strategies
Preventing recurrence is a crucial part of orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers. Long-term use of custom orthotics and protective footwear helps maintain proper foot alignment and reduces pressure points. Managing underlying conditions such as diabetes, neuropathy, and vascular issues plays a critical role in preventing new ulcers. Proper foot hygiene, including daily inspection and gentle cleaning, can detect early signs of trouble. Lifestyle adjustments, like weight management and low-impact exercise, support overall foot health. Patients are encouraged to attend regular follow-ups with an orthopedic specialist to monitor foot mechanics and adjust treatments as needed. Early intervention at the first sign of ulceration significantly reduces the risk of chronic wounds.
What Patients Can Expect During Orthopedic Treatment
Patients undergoing orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers should expect a structured plan that addresses both healing and prevention. The treatment timeline can vary depending on ulcer severity, underlying conditions, and response to therapy. Regular follow-ups allow orthopedists to monitor progress, modify orthotics, or recommend surgical options if necessary. Patients play an active role by adhering to offloading protocols, wearing prescribed footwear, and managing underlying health conditions. Education on proper foot care and activity modification is part of the treatment process. While conservative methods are preferred initially, surgery may be required for persistent or complex ulcers. Understanding realistic outcomes and limitations helps patients remain committed to the treatment plan.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What causes forefoot ulcers to appear repeatedly?
Recurrent forefoot ulcers are often caused by underlying structural deformities, poor circulation, neuropathy, or inadequate footwear. Continuous pressure on specific areas can trigger new ulcers even after previous ones have healed.
How long does orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers usually take?
Healing time varies but generally ranges from several weeks to a few months, depending on ulcer severity, patient health, and adherence to offloading and wound care protocols.
Are orthotics enough to heal a forefoot ulcer?
Orthotics are effective for offloading and preventing recurrence, but severe or infected ulcers may require additional treatments such as debridement, dressings, or surgery.
When should a patient consider surgery for foot ulcers?
Surgery is considered when ulcers do not heal with conservative measures, when structural deformities persist, or when there is risk of infection and tissue loss.
Can orthopedic treatment help diabetics with chronic foot wounds?
Yes, orthopedic treatment, combined with proper diabetic management, is highly effective in promoting healing and preventing further complications.
What type of footwear is recommended for preventing forefoot ulcers?
Protective footwear includes shoes with wide toe boxes, cushioned soles, custom orthotics, and designs that reduce pressure and friction on high-risk areas.
Takeaway
Orthopedic treatment for forefoot ulcers is essential for healing and preventing recurrence, especially in patients with diabetes or structural foot deformities. Combining conservative strategies like offloading, orthotics, and wound care with surgical interventions when needed ensures effective outcomes. Regular follow-up, proper foot hygiene, and lifestyle adjustments are critical to long-term foot health. By understanding the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures, patients can maintain mobility, reduce complications, and enjoy better quality of life through orthopedic care.