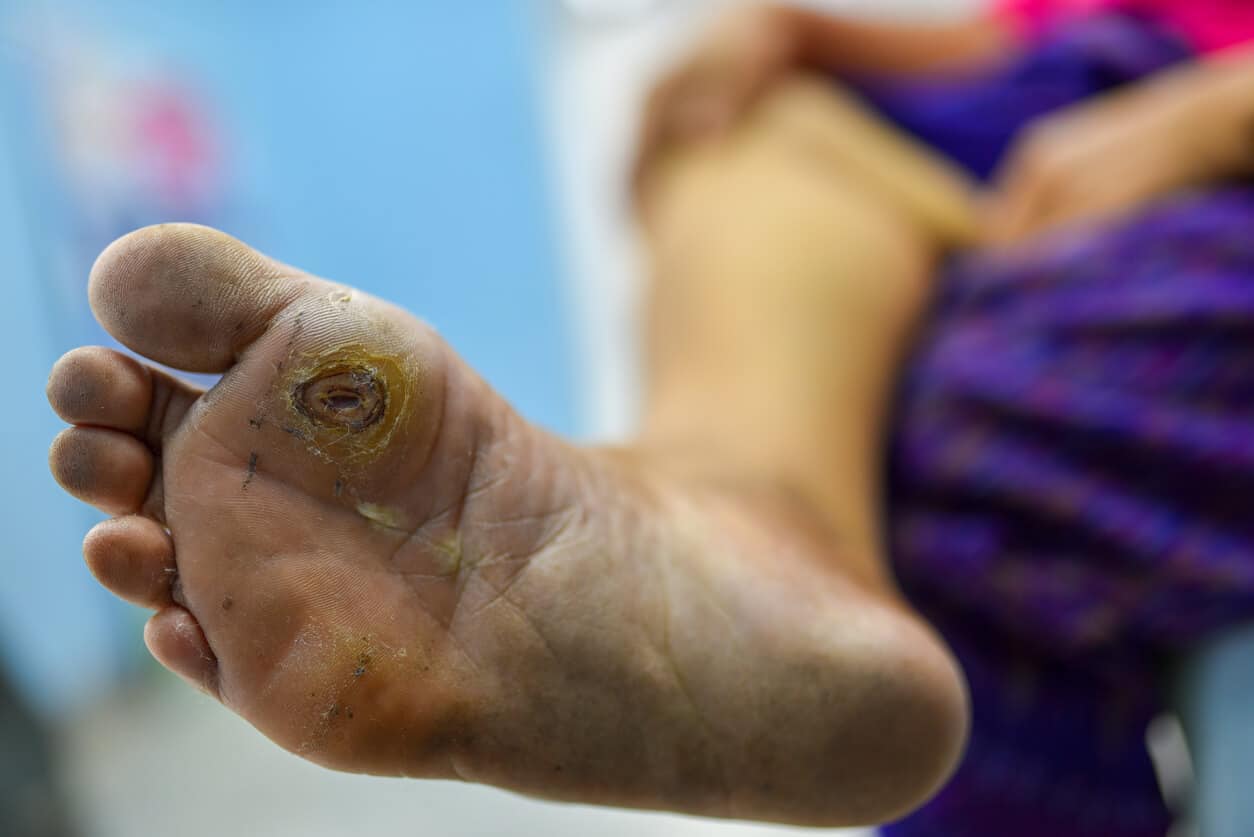
Diabetic gangrene is a serious complication that arises when poor circulation and uncontrolled blood sugar levels cause tissue death. People with diabetes are especially vulnerable because high blood glucose damages blood vessels and nerves, making it harder for wounds to heal. Without adequate oxygen and nutrients, tissues in the feet or toes can break down and become infected, leading to gangrene. Early warning signs include persistent wounds, blackened or discolored skin, swelling, foul odor, and numbness in the affected area. Ignoring these signs can result in rapid progression, where infection spreads to deeper tissues and even bone. What makes diabetic gangrene particularly dangerous is that it often develops silently, especially in patients with nerve damage who may not feel pain. Understanding the seriousness of this condition is the first step toward recognizing the vital role of orthopedic treatment.
The Role of Orthopedic Care in Managing Diabetic Gangrene
Orthopedic specialists play a central role in helping patients with diabetic gangrene manage their condition. Their primary goal is to preserve mobility, reduce infection risk, and when possible, save the affected limb. Orthopedic care does not work in isolation but instead involves collaboration with vascular surgeons to restore blood flow and endocrinologists to stabilize blood sugar levels. By taking a multidisciplinary approach, orthopedic doctors provide patients with a comprehensive plan that addresses both the immediate problem and long-term prevention. Orthopedic expertise is especially important when the infection has reached bones or joints, as this requires precise surgical care and rehabilitation strategies. Without intervention from orthopedic professionals, patients face a higher risk of amputation or severe disability. For many, orthopedic treatment represents hope for retaining independence and maintaining quality of life despite diabetic complications.
Diagnostic Approaches in Orthopedic Treatment
Accurate diagnosis is essential before beginning orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene. The process usually begins with a detailed physical examination and medical history review, where specialists look for signs of tissue damage, infection, and circulation issues. Imaging techniques such as X-rays, MRIs, and Doppler ultrasound scans are commonly used to assess whether bones or soft tissues have been affected. These tools help doctors determine how far the gangrene has progressed and which treatment options will be most effective. Laboratory tests, including blood work and wound cultures, are also crucial for identifying the type of bacteria present and guiding antibiotic therapy. Together, these diagnostic methods provide a full picture of the patient’s condition and allow for precise planning. Without such thorough assessments, treatment would be less effective and might fail to prevent further complications. A timely and accurate diagnosis can often mean the difference between saving or losing a limb.
Non-Surgical Orthopedic Interventions
Not every case of diabetic gangrene immediately requires surgery, and many patients benefit from non-surgical orthopedic interventions. Wound care management is a cornerstone of treatment, involving regular cleaning, dressing changes, and infection control. Specialized dressings can encourage healing while protecting the wound from further injury. Antibiotics are frequently prescribed to prevent the infection from spreading, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be used to stimulate tissue repair by increasing oxygen supply. Orthopedic devices such as custom-made shoes or braces can also help relieve pressure from affected areas, allowing wounds to heal more effectively. At the same time, lifestyle changes are strongly encouraged, including strict glucose control, proper nutrition, and quitting smoking to improve circulation. When followed consistently, these non-surgical measures can slow the progression of gangrene, relieve pain, and enhance overall healing. Patients often find that non-invasive orthopedic treatments improve their ability to manage diabetes-related complications on a daily basis.
Surgical Orthopedic Options for Diabetic Gangrene
When non-surgical treatments are not enough, surgical orthopedic interventions become necessary. Debridement is a common procedure, where surgeons carefully remove dead or infected tissue to stop the spread of gangrene and create a healthier environment for healing. In more advanced cases, skin grafts or reconstructive surgeries may be performed to cover wounds and restore function. Unfortunately, there are situations where amputation becomes unavoidable, particularly if the infection threatens the patient’s overall health. Orthopedic specialists, however, ensure that when amputation is required, it is done in a way that maximizes the patient’s ability to use prosthetics and maintain mobility. Limb-salvage techniques are constantly evolving, with new reconstructive methods aimed at saving as much healthy tissue as possible. These surgical approaches, while challenging, are critical in helping patients avoid life-threatening complications. With expert orthopedic care, even those facing amputation can find pathways to recovery and regain independence.
Post-Treatment Orthopedic Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is an important stage of orthopedic treatment for diabetic gangrene, as it helps patients adapt physically and emotionally after medical or surgical interventions. Physical therapy is often prescribed to rebuild strength, improve circulation, and restore range of motion in affected limbs. Patients who have undergone amputation may work with orthopedic specialists to be fitted for prosthetics, allowing them to return to normal daily activities. Orthotic devices also play a key role in rehabilitation by reducing strain on vulnerable areas and preventing further injuries. Beyond physical healing, rehabilitation includes patient education on foot care, wound monitoring, and diabetes management. Orthopedic teams often work with nutritionists and endocrinologists to reinforce lifestyle habits that promote long-term health. The goal is not only recovery but also prevention of recurring gangrene or related complications. For many patients, this stage of treatment is where they begin to regain confidence and independence after a difficult medical journey.
Preventive Orthopedic Measures for Diabetic Patients
Prevention remains one of the most effective strategies in reducing the risk of diabetic gangrene, and orthopedic specialists play a proactive role in this area. Regular foot screenings allow doctors to detect early warning signs such as poor circulation, minor wounds, or pressure points that could worsen over time. Proper footwear and custom orthotics are recommended to protect feet from injuries that may go unnoticed due to nerve damage. Patients are also advised to inspect their feet daily for cuts, blisters, or unusual changes in skin color. Blood sugar management is emphasized as a cornerstone of prevention, since uncontrolled diabetes dramatically increases the likelihood of tissue damage. Education on healthy lifestyle practices such as balanced diets, hydration, and avoiding smoking can make a significant difference in patient outcomes. Orthopedic doctors also encourage frequent follow-ups to ensure that patients remain on track with preventive care. With consistent attention and proactive measures, many patients can avoid severe complications altogether.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can orthopedic treatment fully reverse diabetic gangrene?
No, once tissue has died due to gangrene, it cannot be restored. However, orthopedic treatment can remove dead tissue, control infection, and preserve as much healthy tissue as possible, significantly improving quality of life.
When should a diabetic patient see an orthopedic doctor?
Diabetic patients should seek orthopedic care if they notice non-healing wounds, changes in skin color, numbness, or swelling in their feet or legs. Early consultation can prevent the condition from worsening.
Are amputations always required in severe diabetic gangrene?
Not always. Amputation is typically considered only when infection or tissue death has spread extensively. Many cases can be managed with debridement, wound care, and reconstructive orthopedic techniques.
How does orthopedic rehabilitation improve quality of life after surgery?
Rehabilitation provides patients with physical therapy, prosthetics, and education to restore mobility and independence. It also equips them with long-term strategies for preventing further complications.
What preventive steps can reduce the risk of developing gangrene again?
Patients can reduce risks by managing blood sugar, wearing protective footwear, inspecting feet daily, and attending regular orthopedic check-ups. Consistency in these habits is vital for prevention.