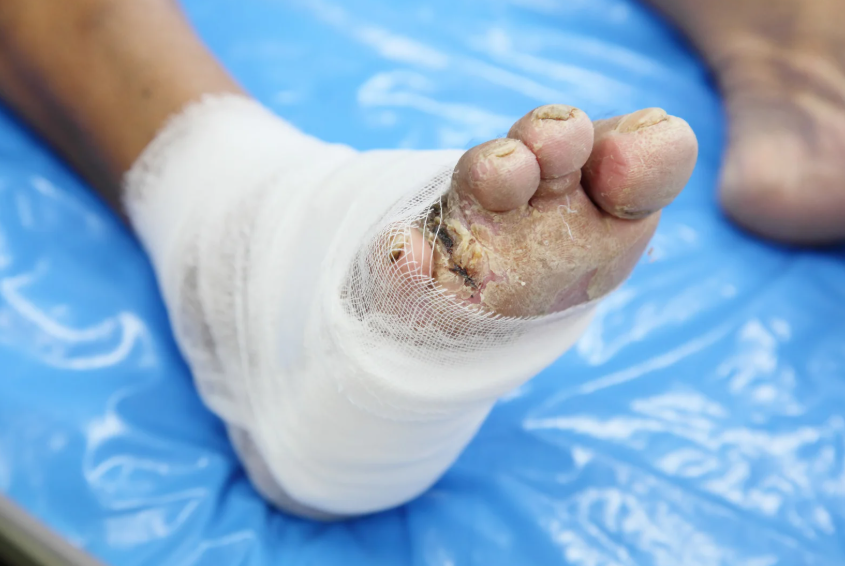
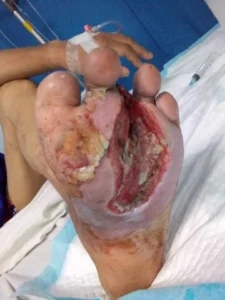
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is essential for patients dealing with chronic wounds that fail to close properly. These wounds, often caused by underlying conditions such as diabetes, poor circulation, or post-surgical complications, can lead to severe infections and long-term health risks. Without timely orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, patients may face complications such as osteomyelitis, amputations, or systemic infections. This article explores the causes, treatment options, and preventive measures to ensure proper wound healing and avoid life-threatening complications.
Understanding Non-Healing Wounds in Orthopedics
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds focuses on managing wounds that fail to close within the expected healing period. Non-healing wounds, also known as chronic wounds, occur due to poor circulation, diabetes, infection, or prolonged pressure on certain body parts. Patients who have undergone orthopedic surgeries are at a higher risk of developing these wounds, especially if they have underlying conditions like peripheral artery disease. By implementing orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds early, patients can reduce the risk of severe infections and other complications.
Common non-healing wounds in orthopedic patients include post-surgical wounds, diabetic foot ulcers, and pressure sores. Each type of wound requires specific orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds to promote healing and prevent infections. Orthopedic specialists assess the wound’s severity and recommend appropriate interventions to enhance recovery. Without proper orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, these wounds may worsen, leading to prolonged hospital stays and additional medical complications.
Orthopedic Approaches to Treating Non-Healing Wounds
Effective orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds involves a combination of medical interventions to promote faster healing. The first step in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is a thorough wound assessment to determine the extent of tissue damage and infection. Orthopedic specialists use advanced diagnostic tools to evaluate the wound and create a personalized treatment plan.
Debridement is a key component of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, involving the removal of dead or infected tissue to stimulate healing. Various debridement techniques, such as surgical, enzymatic, or autolytic debridement, are used based on the wound’s condition. Another effective method in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT), which promotes blood flow and reduces infection risk.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is another approach in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. This method increases oxygen supply to the wound, enhancing tissue regeneration and immune response. In addition, orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds often involves using advanced dressings like hydrocolloid, silver-based, or bioengineered skin substitutes, which create an optimal healing environment.
Preventing Infections in Orthopedic Wound Care
Preventing infections is a crucial aspect of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Infections can significantly delay healing and lead to severe complications such as osteomyelitis or sepsis. The first step in preventing infections through orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is recognizing early signs of infection, including redness, swelling, pain, pus discharge, and fever.
Antibiotic therapy plays a key role in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, as it helps control bacterial infections and prevent their spread. In addition, antimicrobial dressings are often used in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds to reduce bacterial growth and maintain a sterile wound environment. Proper wound hygiene, including regular cleaning and dressing changes, is essential in preventing infections and promoting faster healing.
Another important factor in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is patient education. Patients must be aware of the importance of following their wound care regimen, recognizing signs of infection, and seeking medical attention if complications arise. By adhering to recommended orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, patients can minimize the risk of infections and improve their overall recovery.
Managing Complications in Non-Healing Wounds
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds also involves managing complications that may arise due to delayed healing. If a wound does not respond to conventional treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary. Skin grafts and flap surgery are commonly used in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds to cover large wounds and promote tissue regeneration.
One of the most severe complications that orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds aims to prevent is osteomyelitis, a bone infection that can occur if a wound remains open for too long. When orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds fails to prevent such infections, amputation may become a last resort to save the patient’s life. This highlights the importance of seeking specialized orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds as early as possible.
A multidisciplinary approach is essential in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Collaboration between orthopedic surgeons, wound care specialists, infectious disease experts, and physical therapists ensures a comprehensive treatment plan. By integrating different medical expertise, orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds can achieve better patient outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term disability.
Lifestyle and Rehabilitation for Faster Healing
Lifestyle changes and rehabilitation play a significant role in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Nutrition is a key factor, as adequate protein intake and essential vitamins like Vitamin C and Zinc contribute to tissue regeneration. Proper hydration is also crucial in orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, as it supports cellular function and wound healing.
Physical therapy is an integral part of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, especially for patients with mobility issues. Regular movement helps improve circulation and prevents pressure ulcers. In cases where mobility is limited, orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds includes specialized support, such as pressure-relieving mattresses and assistive devices.
Managing diabetes and circulation issues is another essential aspect of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds. Patients with diabetes must maintain stable blood sugar levels to enhance wound healing. Smoking cessation is also highly recommended as part of orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, as smoking restricts blood flow and delays tissue repair.
Takeaway
Orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds is essential in preventing infections and complications that can arise from chronic wounds. Early intervention, proper wound management, and a multidisciplinary approach ensure better healing outcomes. Patients undergoing orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds must adhere to medical advice, maintain good hygiene, and adopt a healthy lifestyle to promote faster recovery.
By seeking timely orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, patients can avoid severe complications such as infections, amputations, and prolonged hospital stays. With the right orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds, individuals can regain mobility, improve their quality of life, and prevent further medical issues. If you or a loved one is struggling with a chronic wound, consult an orthopedic specialist for personalized orthopedic treatment for non-healing wounds today.